In this post, we discuss the health benefits of acupressure, its history and origin and the tools used in acupressure. We also discuss what acupressure can do to the body as well as acupressure research and studies.
Introduction
With all of the increased stressors in today’s world, it is not surprising that our bodies sometimes experience a variety of aches and pains, including tension and soreness in the muscles. While there are a plethora of modern techniques available for treating these kinds of ailments, there are also various traditional and natural treatments available as well.

One such treatment is acupressure. Acupressure is a type of touch therapy that utilizes the same concepts which underlie acupuncture and Chinese medicine. Acupressure stimulates the same points that are targeted acupuncture. The only difference is that acupressure treatment is applied through the fingers or special tools rather than through the insertion of needles, meaning that acupressure is essentially the non-invasive version of acupuncture. Acupressure has been used for centuries to alleviate various symptoms and sickness and is often performed in conjunction with other traditional Chinese medicine procedures.
Unlike acupuncture, which requires visiting a certified and trained acupuncturist, acupressure can generally be self-performed anytime, anywhere.
What You Need to Know About Acupressure
Fundamentally, acupressure entails applying pressure to the vital healing points of the body. It is believed that these points can stimulate the body’s natural healing capabilities. Pressure is administered primarily through the fingers, but the palms, elbows, feet, or other acupressure tools and devices can be used as well. The word acupressure is a combination of two words - the word “acus”, which in Latin means “needles”, and the word “pressure”.
There are thousands of acupressure points found in different parts of the body. These points are sensitive to pressure and can be in the form of nerve clusters or other sensitive muscles, tendons, ligaments, blood vessels, and veins. These points have two characteristics and manners of function. A point is referred to as “local” when it is stimulated in the same area where pain and tension are felt. The same point can also “trigger” relief in other areas of the body. When one point is stimulated, it is believed that it can deliver healing to the other parts of the body, and alleviate different symptoms and pain.
The concept of “meridians” is also an essential element of acupressure. Meridians are described as the body’s passageway that links the acupressure points to each other and the different organs in the body. Meridians can also be likened to how blood vessels transport blood through the various systems of the body. In the principles of Chinese traditional medicine, meridians are where chi, the vital life energy, travels throughout the body. Acupressure aims to unblock the circulation of chi by stimulating specific points, known as “acupoints”. The meridians closest to the skin is what acupressure seeks to stimulate since these are the easiest to trigger through finger pressure.
History of Acupressure
Acupressure, acupuncture and Chinese traditional medicine are intrinsically linked. Acupressure is believed to have flourished in Asia some 5,000 years ago. The ancient Chinese treatise known as the Huangdi Neijing (The Yellow Emperor’s Classic of Internal Medicine), which emerged around 100 BCE, is said to have first contained an organized system of diagnosis and application of various methods of treatment, among them being acupuncture. It is also during this period that the concept of chi channels (meridians) was developed.
Bronze statues that were discovered dating from the 15th century depicted various acupressure points. These were used for education and examination purposes. Yang Jizhou, a prominent acupuncturist during the Ming Dynasty, compiled the Zhen Jiu Da Cheng (The Great Compendium of Acupuncture and Moxibustion), which describes the origin of acupuncture and other ancient works that are connected to it. This body of knowledge also detailed information related to the human anatomy and the internal organs, and discussed the use of acupuncture in the treatment of diseases.
Different Tools Used in Acupressure
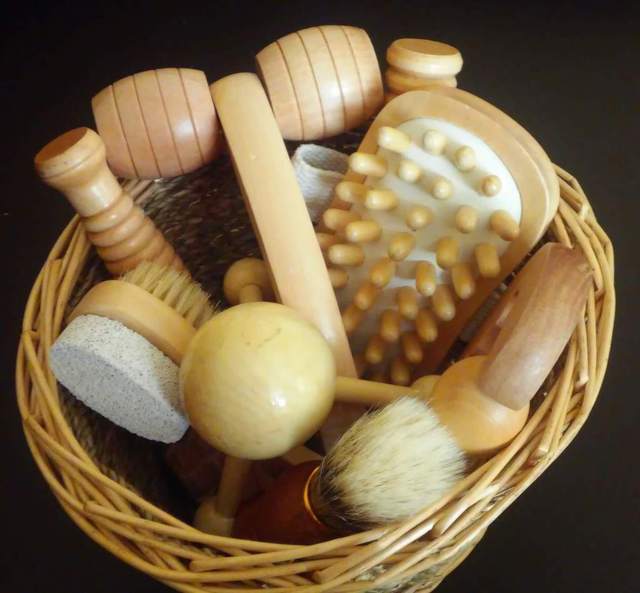

Aside from the fingers, other tools and devices can be used to perform and aid in acupressure:
-
Special magnets shaped into heads of bolts and stars are placed on different acupoints and secured with surgical tape. The magnets can then be easily pressed to trigger the effect.
-
Acupressure mats, hand rollers, foot rollers, thumb pads, and acupressure balls are spiked objects that can be easily used to enjoy a quick acupressure treatment.
-
Acupressure wristbands and bracelets typically have a button or seed stuck to the band. When it is worn, the button is positioned on the P6 (or Nei Kuan) acupoint. Pressing the button stimulates the P6 point, which is believed to help relieve nausea and motion sickness.
There are also other ordinary items that can work as acupressure tools. A tennis ball can be rolled under the foot to experience quick relief by encouraging the feet to assume an arched position. To do this, place the ball under the arch of your foot and move it in circular motions. This movement resembles effleurage, which is a form of a massage using smooth strokes.
What Can Acupressure Do to Your Body?
Acupressure is primarily performed to help alleviate ailments and pains in the body. The health conditions it is used to treat include:
-
Headaches, toothaches, sinus problems;
-
Arthritis;
-
Nausea;
-
Nerve and muscle tension; and
-
Issues with the digestion and the immune system.
Acupressure is even used in beauty treatments to lessen the appearance of wrinkles. It can help increase muscle tone and improve blood circulation in the face and body. The pressure applied during acupressure therapy is believed to help distribute oxygen and give the skin a healthier appearance and help prevent premature skin aging.
In the next section, we canvass various research studies which have demonstrated that acupressure treatment can provide significant health benefits.
Acupressure Research and Studies
Nausea
One research study by Hyde sought to explore the effect of acupressure on pregnant women experiencing morning sickness. The test involved 16 participants who were divided into two groups. The first group wore acupressure wristbands for five days, and went on for another five days without wearing the bands. The second group did the opposite. At the end of the trial, 12 out of the 16 participants reported experiencing relief from nausea and reduced levels of anxiety, depression and behavioral dysfunction.
Another study of acupressure’s effect on nausea was conducted by Chapman et al.The research involved 17 breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. The participants were divided into two groups. The first group was comprised of patients who received acupressure therapy, where the acupoints in the forearm and knee (P6 and ST36) were stimulated through finger acupressure. The other group only received the usual care administered to patients undergoing chemotherapy. The results showed a significant difference between the two groups during the first ten days of the chemotherapy cycle: the women who received the acupressure treatment experienced less nausea compared to the other group.
Anxiety

Acupressure may also be beneficial for people suffering from dyspnoea, a medical condition that involves severe shortness of breath. A study by Tsay et al. explored this link. The study involved 52 patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease who were using mechanical ventilation support. The participants were separated into two groups - one was the experimental group which received acupressure and therapy for ten days, and the other was the control group who only received a massage treatment and handholding. The results showed that the experimental group had improved statistics compared to the control group. The researchers suggest that acupressure can help decrease sympathetic stimulation (the body’s “fight or flight” response) and alleviate the symptoms of dyspnoea and anxiety.
Another study by Barker et al. explored how acupressure affected the anxiety levels of patients who were transported to the hospital in an ambulance. The research involved 38 patients, some of whom received acupressure treatment. Their anxiety and pain levels, blood pressure, and heart rate were measured before the treatment. The participants who received acupressure therapy experienced lesser pain, anxiety, and had a lower heart rate. In addition to these results, the patients reported higher satisfaction with the care they received during the ambulance transport. The researchers encourage health practitioners to consider performing acupressure to help decrease patients’ anxiety and pain during emergency transport.
Dysmenorrhoea
Other research has investigated the effects of acupressure on dysmenorrhoea, which is painful menstruation involving abdominal cramps. The study involved 69 women divided into two groups, one of which received acupressure therapy targeting the sanyinjiao point (which is a point above the ankles). The other group only rested and did not receive acupressure treatment. Results from the test showed that the participants who received sanyinjiao acupressure during the initial session reported reduced levels of pain and anxiety. In addition, a self-treatment follow-up session showed a significant decrease in menstrual pain.
Back Pain
Hsieh et al. conducted a study to determine how acupressure affected chronic back pain. The research involved 129 participants who were experiencing chronic back pain for at least four months. Acupressure therapy was administered to one group, while physical therapy was administered to the other group. The treatments were performed on the participants for one month and they were made to evaluate their experience through certain questionnaires. The results of the questionnaire score after treatment was significantly better with the acupressure group than with the physical therapy group. Results also showed that the acupressure therapy group had a significant reduction of disability than the physical therapy group, and the effects were sustained even after six months as evaluated through a follow-up.
Conclusion
Acupressure has many potential benefits that can improve your health and well-being. However, one should be careful not to completely replace medical prescriptions and methods advised by his or her doctor or medical professional. Always check with a certified health practitioner or seek professional medical advice for any health problems you are experiencing, and disclose any procedures that have been administered to your body.
Did You Enjoy This Article?
Thank you for reading! If you enjoyed this article, you might also like the following articles: Acupressure Points for Stomach Pain and Abdominal Issues and Top 7 Acupressure Points for Nausea Relief

Leave a comment: